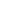
The low flatbed semi-trailer has no railing on the vehicle body and is widely used, mainly for medium and long-distance freight transportation. The series semi-trailer frame adopts a through beam structure, and the longitudinal beam adopts a straight movable goose neck type. The web height ranges from 400mm to 550mm, the longitudinal beam is welded by automatic submerged arc welding, the frame is shot blasted, and the crossbeam penetrates the longitudinal beam and is welded as a whole. Composed of a series of dry plate springs and suspension supports, the structure is reasonable, with strong rigidity and strength, used to support loads and mitigate impacts. Low flatbed semi trailers are usually used to transport heavy vehicles (such as tractors, buses, specialized vehicles, etc.), rail vehicles, mining machinery, forestry machinery, agricultural machinery (such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, pavers, cranes, etc.), and other heavy cargo. The lower the center of gravity, the better the stability and safety, and the stronger the ability to transport ultra-high cargo and pass overhead obstacles. The structure and loading of low flatbed semi trailers usually adopt a concave beam (or well type) frame, with the front section of the frame being a goose neck (the traction pin of the goose neck is connected to the traction saddle on the tractor, and the rear end of the goose neck is connected to the semi-trailer frame), the middle section being the cargo platform (the lowest part of the frame), and the rear end being the wheel frame (including the wheels). When loading mechanical equipment onto a low flatbed semi-trailer, it is usually done from the rear end of the semi-trailer, that is, by moving the mechanical equipment from the rear wheel frame or removing the wheels, and then fixing the mechanical equipment onto the semi-trailer. The walking structure of the low flatbed semi-trailer is made of high-strength international steel material, which has a light weight and ensures its ability to resist torsion, earthquake, and bumps, meeting different road bearing capacities.

Follow us
National Customer Service Line:
Contact Number:
E-mail:
164930313@qq.com
Add:
No. 008, Qingnian Road, Yangzhuangji Town, Yuncheng County, Heze City, Shandong Province, China
Copyright © Shandong Yuncheng Hongdong Special Vehicle Manufacturing Co., Ltd All Rights Reserved